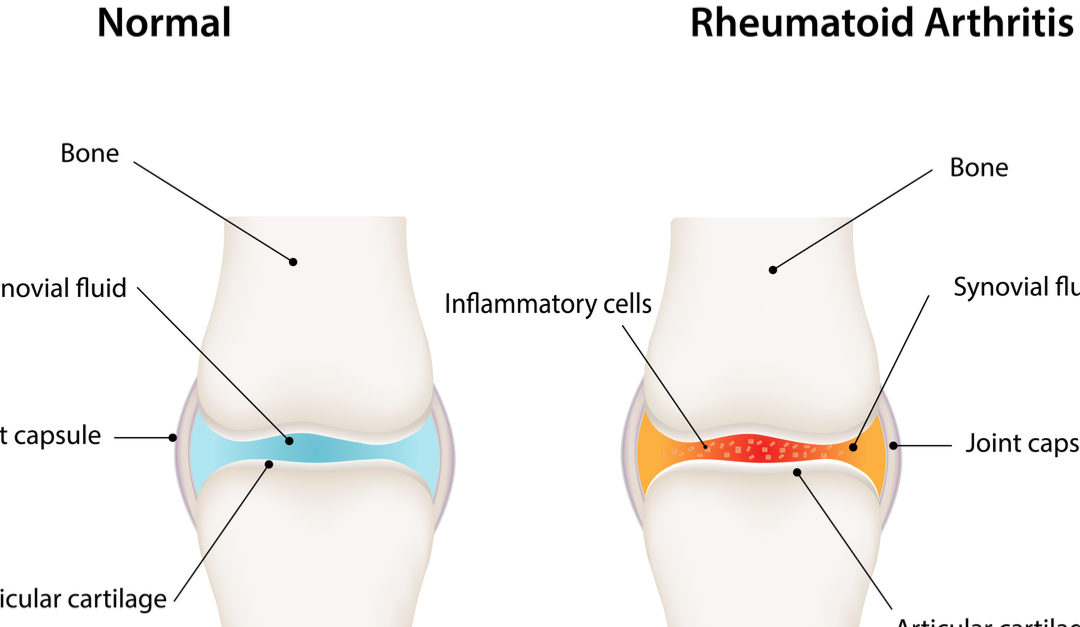
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease in which the body mistakenly mounts an immune attack against its own joints and connective tissues. RA can occur in any joint in the body, but most frequently occurs in those of the hands, feet, wrists, and knees. When left untreated, inflammation caused by RA can damage the cartilage and bone of the affected joint and cause the destruction and premature wear of the articular cartilage on the ends of the bone, resulting in pain and swelling of the joints.
Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The exact cause of RA is unknown. It’s suggested that hereditary, hormonal, and environmental factors may all play a role in the development and progression of the disease.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Initially, patients with RA may not present with symptoms. As the disease progresses, the following symptoms are commonly seen:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Tenderness
- Stiffness
- Visible joint deformities
Additionally, fatigue, loss of appetite, and fever may present. One of the keys to effectively treating RA is an early diagnosis.
Diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Typically a rheumatologist will diagnose and initially treat RA. The first step in an accurate diagnosis involves the taking of a detailed medical history that includes symptoms, medical conditions, and prior injuries. The second step involves a thorough examination of joint(s) affected by RA. Finally, a blood test for antibodies linked to RA and medical imaging studies (x-rays, MRIs, ultrasounds) to better visualize the joint are ordered. After the diagnosis is made, a treatment plan can be decided upon.
Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis
RA is a chronic disease that can’t be cured. The best way to treat RA is to manage its symptoms and prevent its progression. Many medications can be used. They include the following:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Medications that decrease inflammation and pain associated with RA.
- Fast acting anti-inflammatory medications that can be injected into the affected joint or taken orally.
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Medications that slow down the progression of the disease by modifying its course.
- Medications that decrease or stop an immune response by controlling steps in the inflammatory process.
- JAK inhibitors. Medications that inhibit an immune response.
When RA doesn’t respond to nonsurgical treatment and joint mobility and function are impaired, the patient is then referred to an orthopedic surgeon, and joint replacement surgery may be recommended.
Seeking Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis
If you’re experiencing joint pain that won’t go away or if you’ve been diagnosed with RA and have failed to improve with medical treatment with your rheumatologist, please don’t hesitate to contact our offices in Mahwah or Clifton to make an appointment. Dr. Nicholas Alexander is the founder of Mahwah Valley Orthopedic Associates and a Board Certified Orthopedic Surgeon specializing in both the surgical and non-surgical treatment of hip and knee conditions. Dr. Alexander completed his Fellowship in Adult Reconstruction and Reconstructive Surgery of the Hip and Knee at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and has over two decades of experience. He also serves as the Chairman of the Valley Hospital Total Joint Center.